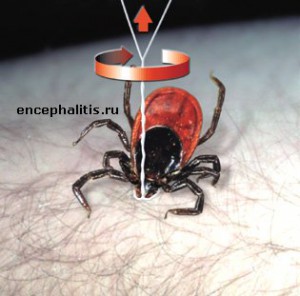
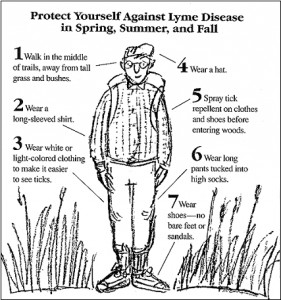
Ticks in Belarus have become a serious problem for tourists. 15 years ago there was no such a problem. Now their number has been greatly increased. The worst thing is that the ticks in Belarus are distributors of dangerous diseases. On the territory of Belarus has been registered only two of them – the tick-borne encephalitis and Lyme borreliosis, or Lyme disease. Human infection occurs mainly through blood by the bite of the tick. But it is possible to be infected by consuming raw goat milk. In the past 10 years in Belarus annually identified 40-120 cases of tick-borne encephalitis and 500-1100 of Lyme disease cases.